Degrees of lateralisation in semantic cognition: Evidence from intrinsic connectivity
Abstract
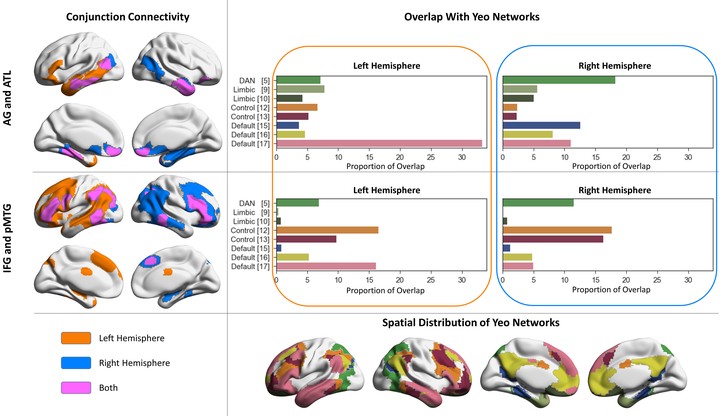
The semantic network is thought to include multiple components, including heteromodal conceptual representations and semantic control processes that shape retrieval to suit the circumstances. Much of this network is strongly left-lateralised; however, work to date has not considered whether separable components of semantic cognition have different degrees of lateralisation. This study examined intrinsic connectivity of four regions implicated in heteromodal semantic cognition, identified using large scale meta-analyses: two sites which have been argued to act as heteromodal semantic hubs in anterior temporal lobe (ATL) and angular gyrus (AG); and two sites implicated in semantic control in inferior frontal (IFG) and posterior middle temporal gyri (pMTG). We compared the intrinsic connectivity of these sites in left hemisphere (LH) and right hemisphere (RH), and linked individual differences in the strength of within- and between-hemisphere connectivity from left-lateralised seeds to performance on semantic tasks, in a sample of 196 healthy volunteers. ATL showed more symmetrical patterns of intrinsic connectivity than the other three sites. The connectivity between IFG and pMTG was stronger in the LH than the RH, suggesting that the semantic control network is strongly left-lateralised. The degree of hemispheric lateralisation also predicted behaviour: participants with stronger intrinsic connectivity within the LH had better semantic performance, while those with stronger intrinsic connectivity between left pMTG and homotopes of semantic regions in the RH performed more poorly on judgements of weak associations, which require greater control. Stronger connectivity between left AG and visual cortex was also linked to poorer perceptual performance. Overall, our results show that hemispheric lateralisation is particularly important for the semantic control network, and that this lateralisation has contrasting functional consequences for the retrieval of dominant and subordinate aspects of knowledge